How To Concept Map
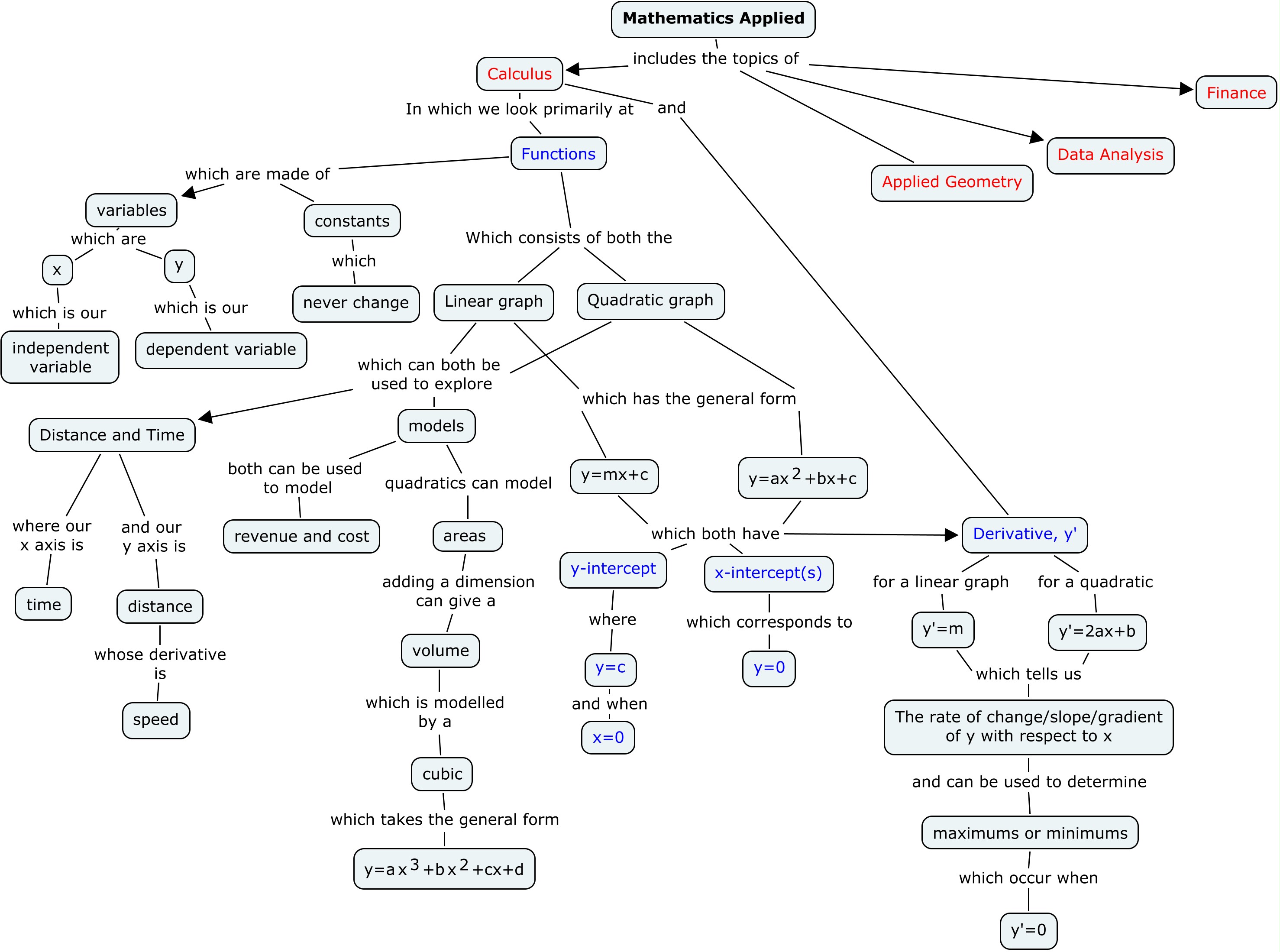
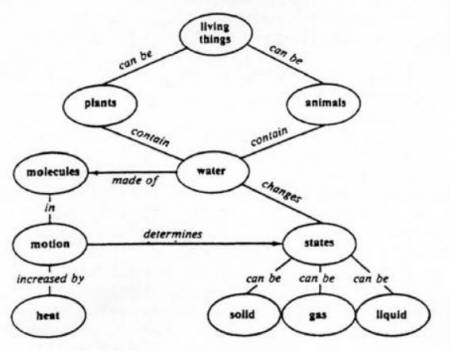
Concept maps are typically made by placing a word in a box or oval and using arrows or lines to link it to other words showing the relationship between these subjects.
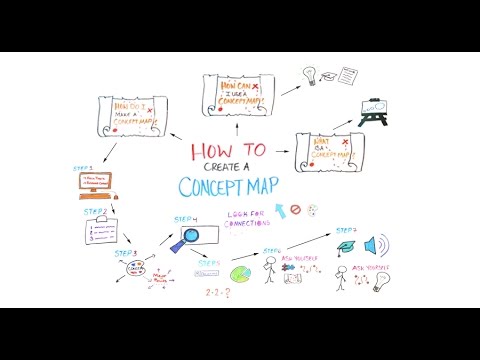
How to concept map. They are also used to show the cross connections between different concepts within one or more main topics. Your concept map will take form as you connect shapes with lines and pinpoint the correct location for each idea. The most common concept maps are the hierarchy concept map the spider concept map and the flow chart concept map. That is a proposition should form a meaningful sentence.
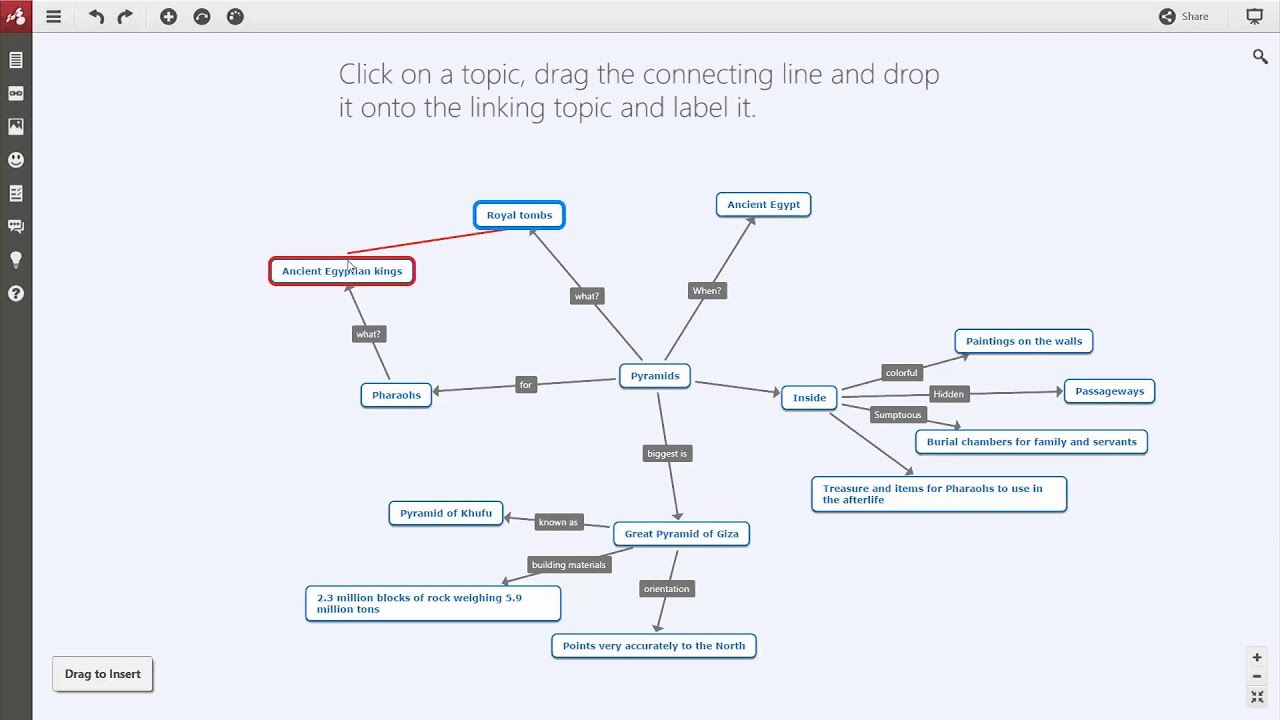
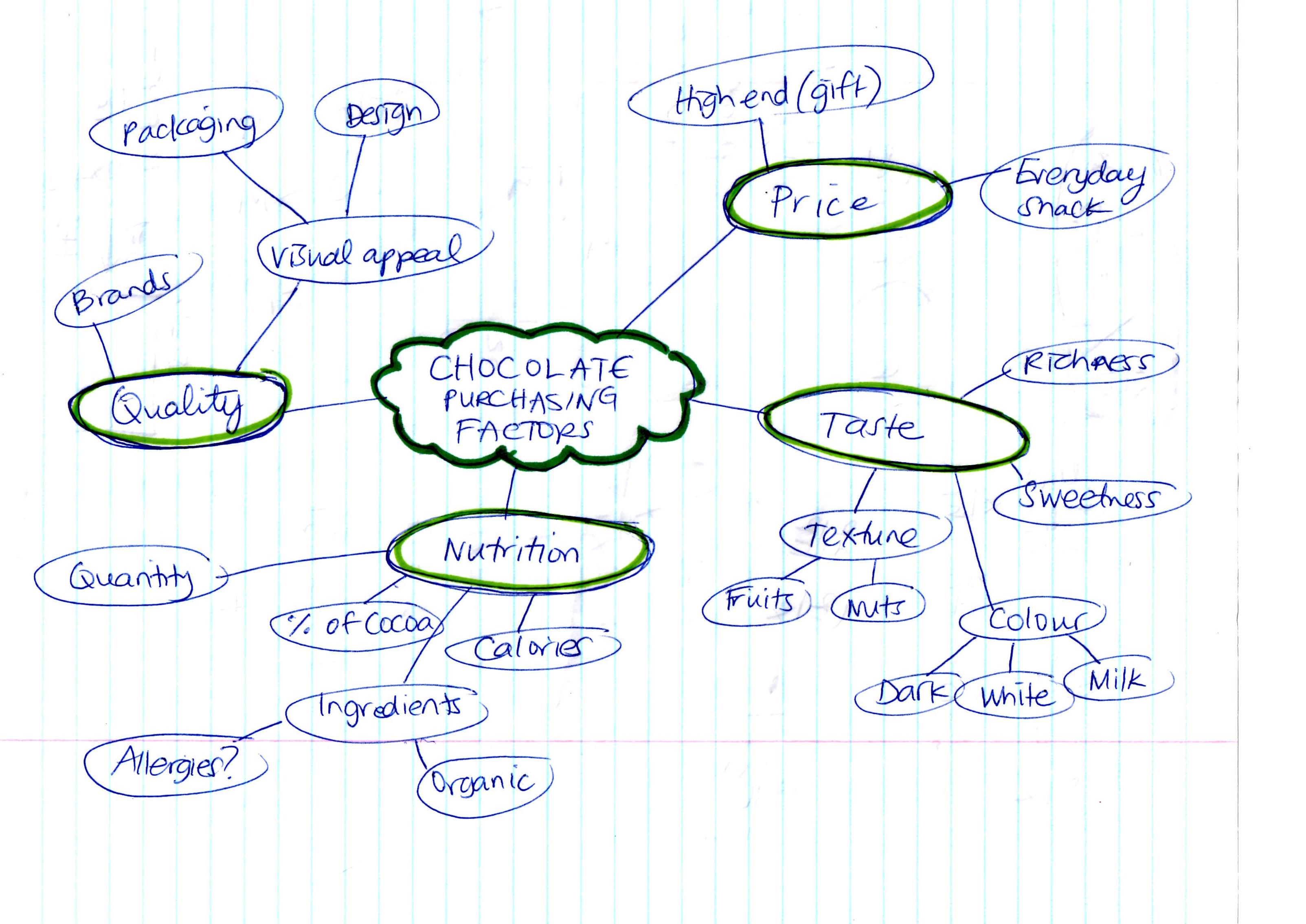
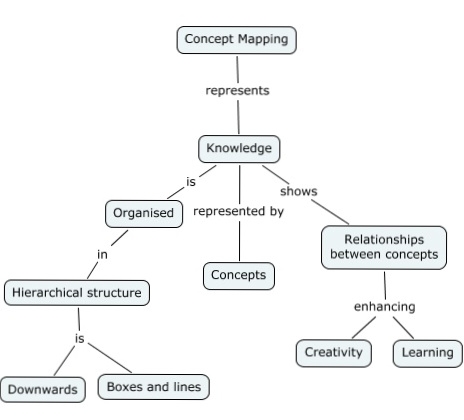
Most concept maps depict ideas as boxes or circles also called nodes which are structured hierarchically and connected with lines or arrows also called arcs. Try mixing things up by using icons images or illustrations to represent ideas. Every two concepts in some cases more than two along with the linking phrases form a meaningful sentence otherwise known as a proposition. Even so every unit is readable.
The goal of a concept map is to simplify complex concepts using circles boxes and all sorts of shapes and icons to represent ideas and lines to connect them together. Concept mapping is an evidence based and a high impact teaching strategy. Order each of your concepts in a hierarchical format with the most general ideas at the top of the map under your main concept and the most specific ones at the bottom. A concept map illustrates a set of meaningful propositions about a topic.
A proposition is the smallest unit of a map. Discover how to make a concept map easily and with the help of an example. A concept map is a graphic tool used to visualize ideas images words or phrases and then organize them in a hierarchical structure. Concept maps are normally used for sorting analyzing and displaying knowledge e g.
But many teachers and students are unsure how to make a concept map easily. What is a concept map. A review of meta analytic research shows that concept mapping has a typical impact of d 0 66. When to use a concept map.
Tacit information etc and problems based on a large and complex set of information.